Our Products
Solar PV power generation systems are suitable for residential, commercial, and utility-scale applications. The size of the system can vary depending on energy needs and available space.
System Structure Drawing
Grid-connected photovoltaic power generation is the direct current generated by solar modules through grid-connected inverters into AC power in line with the requirements of the mains power grid and then directly connected to the public power grid. It can be divided into grid-connected power generation systems with and without batteries.
The off-grid photovoltaic system is mainly composed of solar cell modules, controllers, and batteries. To power AC loads, AC inverters are also required.
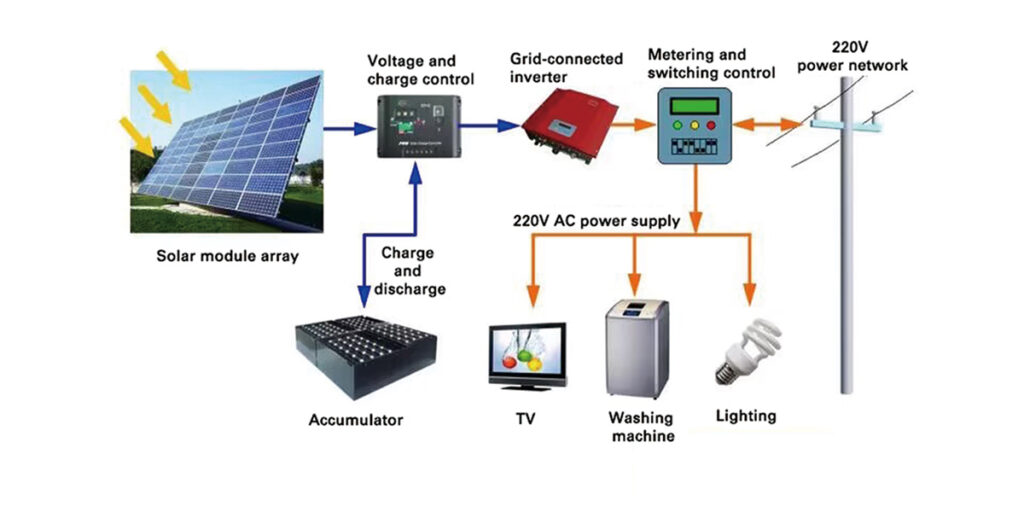
Here’s how a typical solar PV power generation system works:
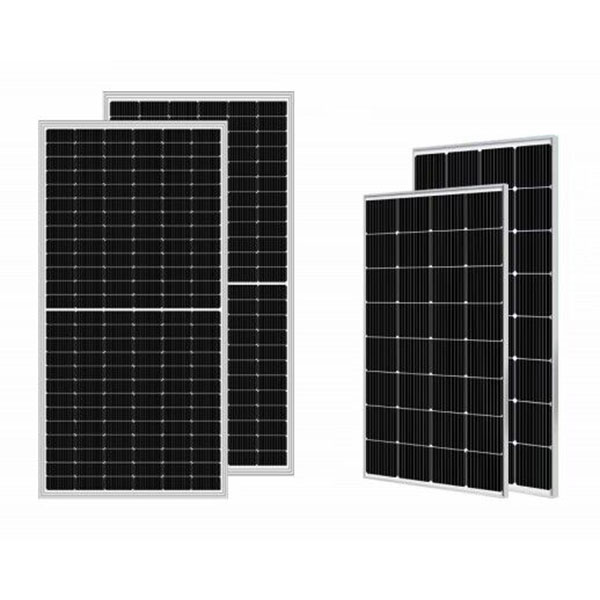
- Solar Panels: The system starts with solar panels, also known as solar modules or solar arrays. These panels consist of multiple photovoltaic cells made of semiconductor materials, typically silicon. When sunlight hits the panels, the photons in the sunlight excite electrons in the cells, creating a flow of DC (direct current) electricity.
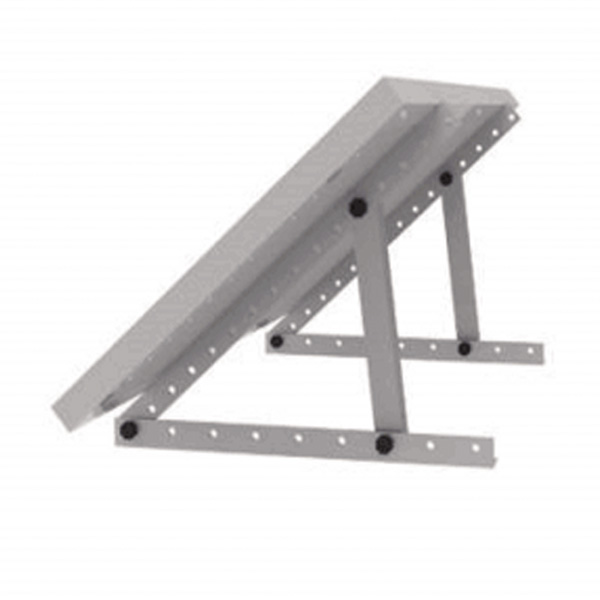
- Mounting and Orientation: The solar panels are typically mounted on rooftops, ground-mounted racks, or integrated into building materials like solar shingles. The panels are strategically oriented to maximize sun exposure and capture as much sunlight as possible throughout the day. Optimizing the tilt and azimuth angle helps maximize energy production.
- Inverter: The DC electricity generated by the solar panels is then converted into AC (alternating current) electricity using an inverter. AC electricity is the standard form of electricity used in homes and businesses.
- Electrical Panel and Grid Connection: The AC electricity from the inverter is sent to the electrical panel of the building. It can be used to power electrical loads directly, such as lights, appliances, and other devices. If the solar system produces more electricity than what is currently being consumed, the excess power can be fed back into the electric grid. This process is known as net metering or grid-tied system.
- Net Metering and Grid Integration: In a grid-tied solar system, when the solar panels generate more electricity than the building needs, the excess power is sent back to the grid. The utility company credits the surplus electricity, effectively spinning the electric meter backward. During times when the solar system isn’t producing enough power, electricity is drawn from the grid to meet the demand.
Benefits of a solar PV power generation system:
- Renewable and Clean Energy
- Cost Savings
- Low Maintenance
- Energy Independence
- Long-Term Investment
Separated MPPT Power Frequency OFF Grid Power System
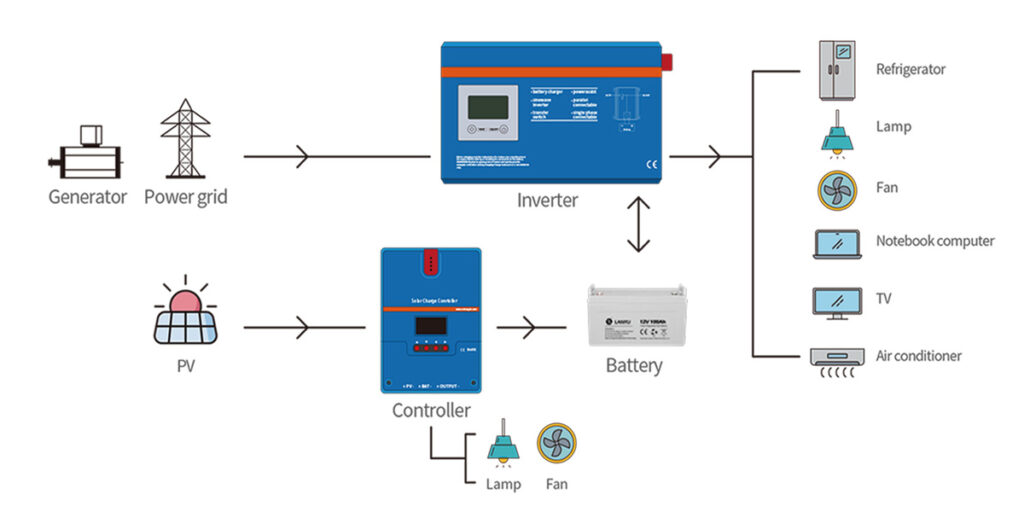
However, there are requirements for access to the grid. If not, off-grid can be used.
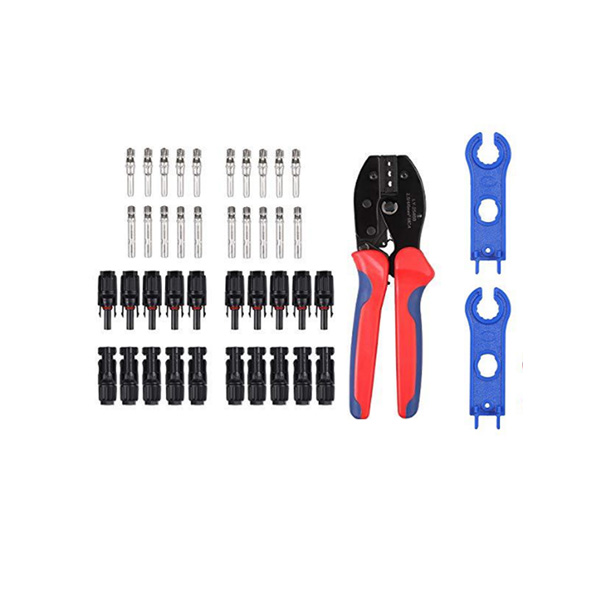
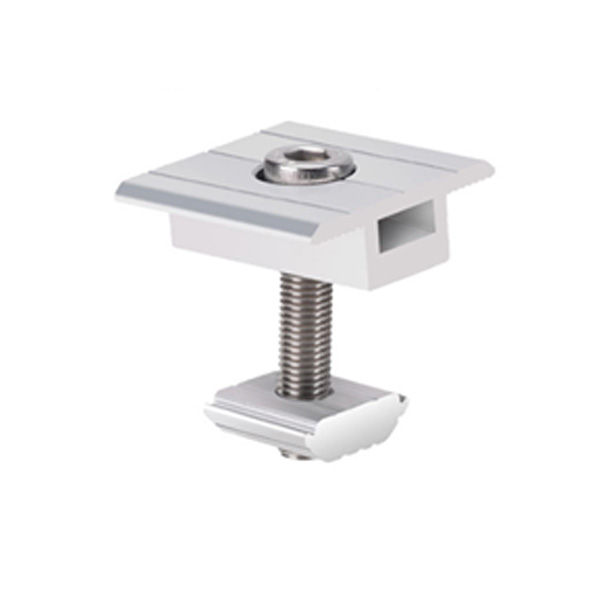
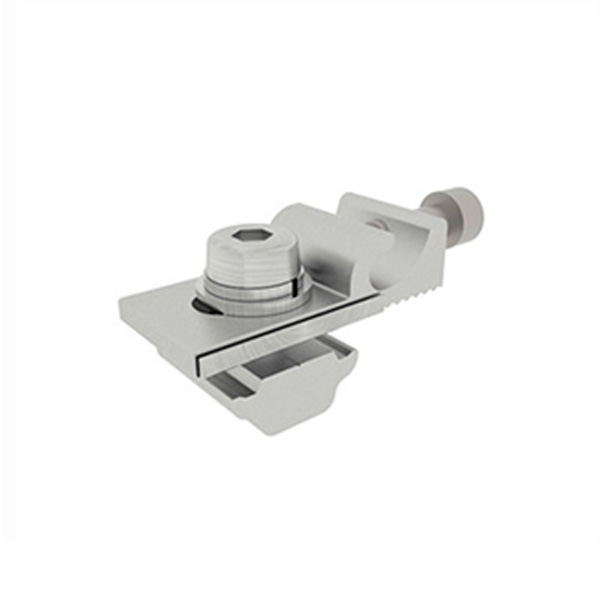
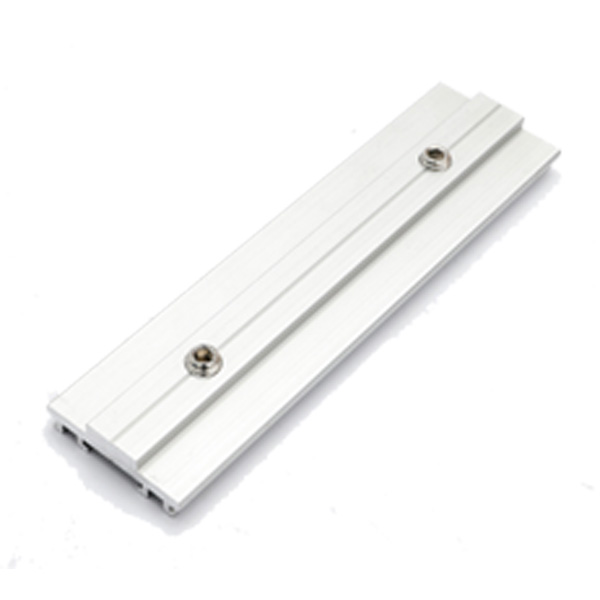
Accessories